March 4, 2025
Ever wonder why bouncing back from a tough workout takes longer as you age—or why building muscle and recovering from soreness feels more challenging than it used to?
The answer lies in one of your body’s most powerful regenerative tools: stem cells. These microscopic repair agents are essential for recovery, muscle growth, and even slowing the aging process. When abundant, they work to regenerate damaged tissues, reduce inflammation, and rebuild muscle efficiently.
The catch? As people age, your stem cell count significantly declines, making recovery and regeneration more difficult.
By the time you hit your 30s, your stem cell reserves decline dramatically—up to 80%—and keep dwindling as you get older. This loss affects more than just workout recovery—it hampers your body’s ability to heal from injuries, repair muscle microtears, and recover from the oxidative stress brought on by intense exercise.
Without enough stem cells in circulation, your body struggles to keep up with the wear and tear of daily life, let alone the damage caused by heavy lifts, sprints, or endurance sessions. The result? Longer recovery times, persistent soreness, and an uphill battle to maintain peak performance.
Fortunately, research in stem cell science, pioneered by stem cell scientist Christian Drapeau, has revealed solutions that can enhance your body’s innate repair system. Drapeau has spent over 23 years researching stem cells and has traveled the world in search of natural alternatives that can enhance your stem cells, which is especially important if you can't necessarily find or afford stem cell IV's or injections (which I've shared by personal experience with here), or want to keep your levels topped up in between stem cell treatments (learn more about stem cell therapy here).
Drapeau's research has found that increasing the number of circulating stem cells can support your ability to repair muscles faster, reduce inflammation, and even slow the aging process.
Increasing stem cell circulation isn’t just about being able to work out harder or recover faster—it’s about biohacking your biology to feel younger, stronger, and more resilient every day. In this article, you’ll discover the science behind how stem cells work, why they’re essential for recovery and longevity, and how you can naturally increase your circulating stem cells using cutting-edge natural products.
If you’re ready to train harder, recover faster, and hack the aging process, you’re in the right place.
Key Takeaways You'll Discover
- Lactic acid’s role in muscle repair: Lactic acid isn’t the cause of muscle soreness but acts as a signaling molecule that activates satellite cells (muscle-specific stem cells) to repair microtears and promote recovery, strengthening the tissue over time.
- Stem cell decline with age: Aging reduces the number of mesenchymal and hematopoietic stem cells, slowing down tissue repair, recovery, and energy levels. This decline also impacts longevity and performance, making stem cell optimization crucial for staying fit and resilient.
- Boosting recovery and performance with stem cells: Increasing circulating stem cells enhances muscle repair, reduces inflammation, and improves strength and endurance, offering a significant advantage for faster recovery and better overall fitness (you can read more about my own self-experimentation with a full body stem-cell makeover here).
- Stem cells and muscle recovery science: Stem cells repair damaged muscle fibers, modulate inflammation, and regenerate tissues throughout the body. They also reduce oxidative stress, contributing to faster recovery and long-term health benefits.
- Not all stem cells are equal: Different stem cells serve different functions. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) repair muscle, bone, and connective tissue, while hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) regenerate blood and immune cells. Understanding their roles is key to leveraging their healing potential.
- Natural ways to boost stem cell production: Strategies like fasting, exercise, and specific dietary changes can naturally increase stem cell counts. Advanced methods, including hyperbaric oxygen therapy and certain peptides or supplements, can elevate circulating stem cells by up to 10 million in just hours, enhancing recovery and regeneration.
Why Am I Sore After Strength Training? Understanding the Stem Cell Connection
One of the biggest fitness myths is that lactic acid causes muscle soreness.
This idea has been floating around gym locker rooms and fitness forums for decades, but it’s time to set the record straight.
Lactic acid isn’t the villain you think it is. In fact, it’s not even a waste product as many have previously thought. Several studies have debunked the theory that lactic acid builds up in your muscles post-workout and causes soreness.
Here’s the truth: lactic acid, or lactate, is *actually* a fuel source for your cells during anaerobic exercise—when your body is working so hard it can’t get enough oxygen to meet demand. Lactic acid is produced when your body breaks down glucose for energy and is then cleared from the muscles shortly after exercise.
And here’s where things get fascinating: instead of causing pain, lactate plays a critical role in signaling your body to kickstart the recovery process by activating stem cells and other repair mechanisms.
The Real Reason for Soreness: Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS)
If lactic acid isn’t to blame, what’s behind that next-day soreness after a brutal leg day—the kind that turns a simple flight of stairs into a full-blown endurance challenge?
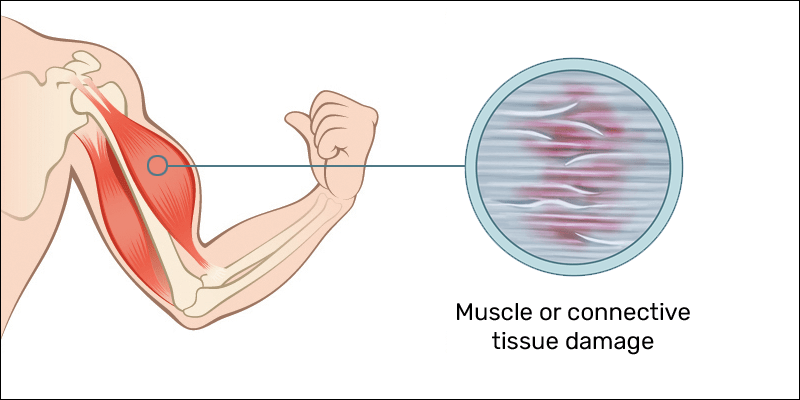
The answer lies in micro-tears and inflammation in the muscles.
Pushing your muscles through intense or unfamiliar physical activity, especially during eccentric contractions (think lowering a heavy weight or downhill running), creates tiny tears in your muscle fibers. These muscle tears are what trigger an inflammatory response, not lactic acid.
This inflammation, known as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), typically sets in 24–48 hours after your workout and can last anywhere from a few days to a week. Unlike the immediate pain of a strain or injury, DOMS is part of your body’s natural recovery process, signaling repair and adaptation to the stress you’ve placed on your muscles. The extent of this inflammatory response depends on the intensity of your workout, its duration, and the specific muscles being exercised (for more information, you can check out my article about DOMS here).
Connecting Lactic Acid, Muscle Soreness & Stem Cell Activation
While lactic acid doesn’t cause soreness, it does play a behind-the-scenes role in your body’s repair and recovery game plan.
When lactate levels rise during intense exercise, it helps trigger the release of key signaling molecules that mobilize stem cells—your body’s innate repair system. These stem cells then travel to the damaged muscle fibers, reducing inflammation, repairing tissue, and even promoting muscle growth.
So, instead of blaming lactic acid, think of it as one of your critical players in the chain reaction that helps you recover faster and get stronger. This natural process is essential for post-workout recovery and overall muscle health and longevity.
In the next section, you’ll dive deeper into what stem cells do in your body and how they help your body repair sore muscles and help you recover faster.
What Are Stem Cells and How Are They Connected to Muscle Repair and Recovery?
To understand stem cells and their importance, it’s helpful to first distinguish them from other cells in the body.
Most cells, known as somatic cells, are specialized for a single purpose and cannot change or replicate indefinitely. These specialized cells will perform their specific role until they naturally die off and are replaced.
Stem cells, on the other hand, are unique because they are “unspecialized” and have two key abilities: self-renewal (the ability to replicate themselves indefinitely) and differentiation (the ability to transform into various types of specialized cells). Their unique abilities make them an essential component of the body’s natural repair system.
Unlike somatic cells, stem cells are not fixed to a single function, allowing them to respond dynamically to the body’s needs, whether it’s healing tissue damage or creating new cells.
Stem cells are your body’s natural repair system, springing into action when your muscles sustain microtears (DOMS) from a tough workout or injury. These powerful cells repair damaged tissue, reduce inflammation, and even fuse with muscle fibers to promote growth and strength. By boosting your circulating stem cells, you supercharge your body’s natural ability to recover faster, train harder, and build stronger muscles.
Types of Stem Cells
There are several types of stem cells you’ve probably heard of, each with unique properties:
- Embryonic stem cells (ESCs): Found in early-stage embryos, these cells are pluripotent, meaning they can transform into any cell type in the body. ESCs are not present after birth and are typically obtained through medical interventions (called in vitro fertilization or IVF).
- Adult stem cells: Naturally occurring in all living organisms, these stem cells are found in reservoirs like red bone marrow, fat, and blood, but they are present in almost all tissues, including skin, liver, lungs, brain, heart, and muscle (read more about how stem cells are harvested here). These stem cells have the unique ability to replicate themselves and transform into other types of cells with different functions, a process called differentiation.
- Umbilical cord and placenta stem cells: Derived from newborns’ umbilical cord or placenta, these cells are considered adult stem cells. They are also multi-potent and show promise for therapeutic applications. For additional information, you can listen to my podcast on umbilical cord stem cells here.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): These are normal cells—usually skin cells—pulled from a patient and then genetically reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells. These stem cells are capable of transforming into any cell type. However, this is an evolving science; due to the risk of tumor formation, iPSCs have not yet been utilized to treat humans.
- Muse cells or X cells: Muse cells are a unique, stress-resistant type of stem cell found in both bone marrow and adipose tissue. As pluripotent cells, they have the ability to transform into any cell type needed, making them powerful agents of repair. These resilient cells thrive even in challenging environments, supporting the survival of damaged or injured tissues. I’ve written more about these here.
Stem cells are at the forefront of cutting-edge science when it comes to enhancing your body’s ability to recover, repair, and grow stronger. While there are countless treatments available that boost stem cell function, ranging from injections to lab-engineered options, the truth is your body already has its own natural reservoir of adult stem cells.
These powerful cells are found in your red bone marrow and various tissues throughout your body (including adipose tissue, or fat, which you can learn more about here), acting as your body’s built-in repair system, ready to mobilize 24 hours a day when damage occurs to muscles or other tissues.
What sets these natural stem cells apart is their incredible versatility. They don’t just help heal microtears or reduce inflammation after a challenging workout—they also actively promote muscle growth by integrating with muscle fibers, creating stronger and more resilient tissue. Even better, you can naturally activate and mobilize these stem cells without resorting to costly or invasive treatments.
Bone Marrow Adult Stem Cells: The Body’s Natural Muscle Repair System
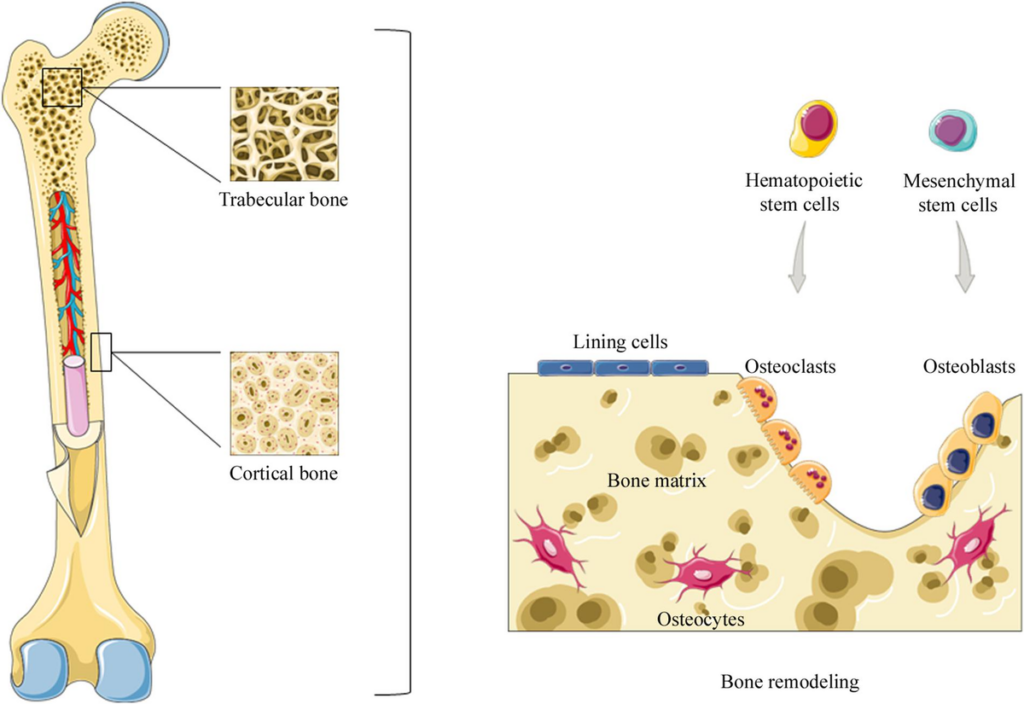
For years, science primarily recognized bone marrow stem cells for their critical role in the constant renewal of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, as well as the regeneration of bone, ligaments, tendons, and connective tissue.
However, groundbreaking discoveries at the turn of the century revealed that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)—a specific type of adult stem cell found in bone marrow—have far greater potential.
These versatile cells can transform into a variety of cell types, including those found in the heart, brain, liver, pancreas, and, yes, muscle tissue. This discovery solidified the understanding that bone marrow stem cells are not just blood-cell factories but are the cornerstone of the body’s system of repair and renewal.
Mesenchymal adult stem cells are leading the way in groundbreaking research on tissue regeneration, muscle repair, and fighting age-related conditions.
Unlike somatic cells, which are specialized and fixed in their function, MSCs have the unique ability to differentiate into a wide range of cell types. This means they can repair and regenerate tissues in critical systems like the immune system and in those of the brain, skin, liver, and muscles. Their regenerative power plays a pivotal role in maintaining and repairing tissues, accelerating muscle recovery, and alleviating soreness caused by the microtears that occur during intense workouts.
Why Does Recovery Slow as You Age, Despite the Power of Mesenchymal Stem Cells?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are undeniably powerful in their ability to repair muscle and tissue, so why does recovery from workouts and injuries take longer as you age?
The answer lies in the gradual decline of red bone marrow, which produces these vital stem cells. This decline sets off a cascade of changes that weaken the body’s ability to heal, recover, and maintain overall health.
With fewer MSCs circulating in the bloodstream, microtears in muscle fibers—caused by intense workouts—heal more slowly, inflammation lingers longer, and soreness becomes a persistent issue.
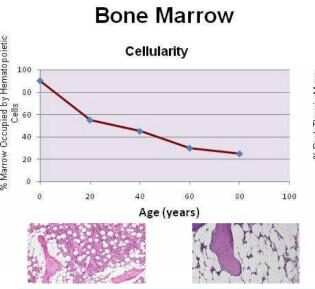
By the age of 30, approximately 80% of your MSC supply is depleted due to this progressive replacement of red bone marrow with adipose-rich yellow bone marrow, which cannot produce stem cells.
This replacement quickly takes place in the long bones (in the arms and legs), reaching essentially 100% conversion by age 25, and then more slowly in other areas, such as the ribs, breastbone, shoulder blades, collarbones, hip bones, skull, and spine. The resulting decline in red bone marrow leads to a roughly 80% overall reduction in circulating MSCs, significantly impairing the body’s ability to repair and regenerate tissues.
This loss of regenerative capacity manifests as slower muscle recovery, reduced strength, and increased susceptibility to injuries. Over time, this process contributes to both the visible signs of aging, like diminished stamina, and the unseen effects, such as a decreased ability to repair tissues across the body.
Despite this decline in your stem cell supply and its effectiveness, MSCs still remain effective as the body’s innate repair system. These cells retain their regenerative potential and can duplicate and repair damaged tissues, including muscle fibers affected by microtears.
The challenge, then, is not their effectiveness but their availability. As you age, it’s important to release more of these stem cells and increase their circulation to enhance recovery, reduce inflammation, and rebuild tissues more effectively.
Increasing your number of circulating stem cells, even with a reduced overall reservoir, you can see both immediate and long-term benefits.
In the short term, muscle recovery accelerates, and inflammation subsides more quickly. Over the long term, increased stem cell activity promotes muscle growth, strengthens tissue resilience, and supports overall health and vitality.
This proactive approach enables you to recover faster, train harder, and maintain an active lifestyle well into your later years, making it a cornerstone of performance and longevity.
Before I talk about how to increase your circulating stem cells, I want you first to understand the science behind how these stem cells actually repair and grow your muscles after intense workouts.
Behind the Scenes of Muscle Recovery: The Science of Stem Cell Muscle Repair and What’s Really Happening
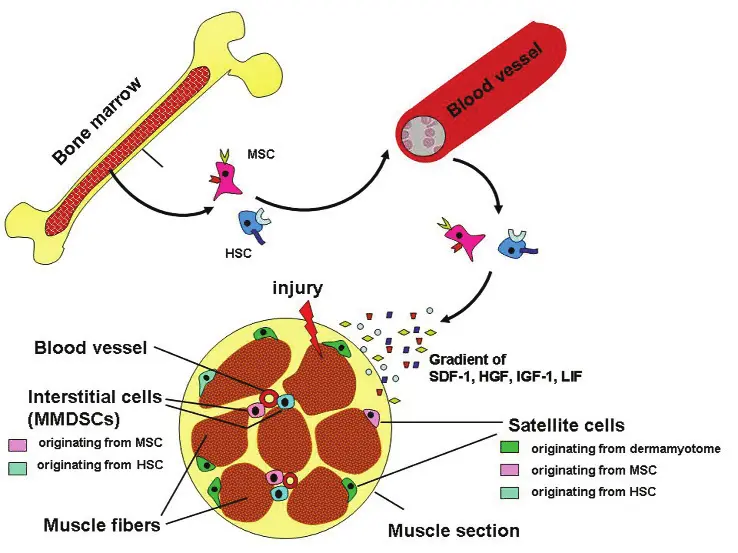
When your muscle tissue sustains micro-tears or injuries—like those caused by intense workouts—your body relies on an intricate repair system involving both local muscle stem cells (known as satellite cells) and stem cells from bone marrow.
If the satellite cells at the injury site are insufficient to fully repair the damage, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from your bone marrow are mobilized to step in and assist with the healing process.
This dynamic repair system also depends on a carefully orchestrated cascade of chemical signals. These signals, released in response to muscle damage, trigger a combination of inflammatory, anti-inflammatory, and nociceptive (pain-modulating) responses, all of which work together to guide stem cells to the injury site. The MSCs flow through the bloodstream, then migrate into the damaged muscle tissue, and begin their work—reducing inflammation, repairing tissue, and promoting muscle fiber growth.
The speed and efficiency of this repair process are directly tied to the number of circulating stem cells available. The more MSCs are mobilized from your bone marrow, the faster the muscle heals, soreness is alleviated, and muscle growth is enhanced.
This natural, biology-driven mechanism is critical for recovery and building stronger, more resilient muscles that can handle greater loads in the future.
You can discover more about stem cells by listening to some of my podcasts:
- Get The MOST Out of Stem Cells By Stacking Ozone, Peptides, Exosomes, Lasers, & More With Dr. Joy Kong
- Lightning Speed Healing Hack or Overpriced Fad? What You Need to Know About Stem Cells
- Age Reversal In Mexico: Follistatin & Klotho Gene Therapy, The Right & Wrong Kind Of Stem Cells, NK Killer Cell Infusion, Nerve Blocks & More With Adeel Khan
The Signal Highway: How Your Body Guides Stem Cells to Damaged Muscle Tissue
Stem cells rely on several sets of chemical signals to alert them to first be released from the bone marrow and then give them directions on where to go.
These chemical signals are cytokines. Cytokines are small protein molecules that are crucial in controlling the mobilization and activity of immune cells. When released, they signal the immune system to do its job, which includes releasing stem cells.
Shortly after a muscle injury, due to strength training, the affected tissue begins to secrete the cytokines, namely granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) and stem cell factor (SCF), triggering an increase in the number of circulating stem cells. Within 3–5 days of a significant injury, like a heart attack, muscle tear, ligament tear, or bone fracture, the number of circulating stem cells increases three to tenfold.
After strength training, your muscles, tendons, or ligaments can experience micro-tears, and the body sends out other distress signals that trigger pro-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory, and nociceptive responses using cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-𝛂), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin-10 (IL-10), and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra).
Soon after, another signaling cytokine called stromal-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) is also released locally by the affected tissue. The purpose of SDF-1 is to attract stem cells to the area of the muscle injury or micro-tears due to an intense workout. As stem cells circulate through the bloodstream and pass through the fine capillaries of the injured tissue, binding of SDF-1 to its specific receptor CXCR4 at the surface of stem cells triggers the expression of adhesion molecules, causing the stem cells to adhere to the capillary wall.
The continued presence of SDF-1 then triggers extravasation, the process by which stem cells move through the capillary wall from the bloodstream into the tissue.
Upon arriving in the tissue and coming in contact with cellular debris (organic waste left over after a cell dies or when a muscle is injured), the stem cells first shut down inflammation. Then, they begin to multiply and transform into the specific cells of that tissue, effectively repairing it.
As the muscle tissue is repaired, your body begins the muscle growth process and builds muscle strength. This happens through the fusion of satellite cells (muscle stem cells) with muscle fibers. The growth of your muscle after a workout depends on the number of satellite cells available to participate in this process of cellular fusion. By putting more stem cells in circulation, more stem cells are available to replenish the satellite cell population and support muscle recovery and growth.
In this entire tissue repair process, the most studied and relevant factor is understanding that the number of circulating stem cells directly impacts (positivity or negativity) tissue repair and overall health.
More circulating stem cells mean greater availability of these cells to participate in tissue repair and enhance the healing process. This means shorter moments of soreness and quicker recovery after strength training or other intense workouts.
Discover How to Boost Your Circulating Stem Cells for Faster Muscle Recovery & Better Gains After Workouts and Injuries
Now that you know how powerful your body’s adult stem cells are in helping your muscles repair, recover, and grow after tough workouts or injuries, you’re probably wondering how to unlock their full potential.
Even though your stem cell supply naturally decreases with age, finding ways to mobilize and boost these cells can give your body a serious advantage in recovery and regenerative potential.
So, the next big question is: how do you make this happen?
Can you actually boost your stem cells in a practical, effective, and sustainable way? The answer is yes, and I will dive into stem cell injections but, more importantly, an alternative to injections–science-backed natural products that make stem cell support more accessible.
You have probably already heard about stem cell injections and how they offer a direct and effective method of increasing the number of stem cells circulating in the bloodstream (I’ve talked about stem cell injections previously here and here).
This process typically involves harvesting stem cells, either from the patient’s own body (from bone marrow or adipose tissue) or from a donor. Donor stem cells, which can be derived from sources such as umbilical cord or placenta tissue, provide a rich supply of pluripotent or multi-potent stem cells–giving them a high level of differentiation.
Once injected, these stem cells have the ability to become virtually any type of cell, allowing them to repair any tissue in the body. Stem cell injections may be a viable option for chronic conditions or substantial injuries, but injections are both expensive and regulated in the U.S. (read more about the FDA regulations here). Therefore, it isn’t feasible for most people to do an injection every intense workout because each treatment can cost anywhere from $2000–$20,000 or more.
For most people, stem cell injection treatments are simply too expensive to do regularly, making them an unsustainable option for boosting circulating stem cells. To learn more about stem cell injections, you can check out my deep dive into them here.
An Everyday, Affordable Solution: Natural and Noninvasive Stem Cell Support
Stem cell researcher and founder of STEMREGEN, Christian Drapeau (mentioned earlier in this article), was the first to discover unique plants that support the natural function of the adult stem cells in your body.
Drapeau proposed and published the hypothesis that stem cells constitute the “repair system” of the body in his peer-reviewed Medical Hypotheses article in October 2002 and expanded on the idea in the first edition of his breakthrough book, Cracking the Stem Cell Code, published in 2010. These findings made him the first scientist to name a new bodily system since the early 1900s. Owning nine patents related to stem cells, he has spent over 23 years conducting research to better understand the role stem cells play and identify ways to improve the performance of the body’s repair system, the foundation of regenerative medicine. 
Drapeau discovered that just like many plants have been documented to support the immune system, there are several plants that have been found to support the repair system by increasing the number of circulating stem cells from the bone marrow. STEMREGEN products and ingredients have had numerous research studies documenting their effectiveness in supporting stem cells, including randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled human clinical trials (you can check out some of these studies here and here).
Drapeau has traveled the world to discover natural plants that support stem cell mobilization, such as sea buckthorn berry, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (AFA), Aloe macroclada, and fucoidan from seaweeds, just to name a few. Some may dismiss these natural ingredients because they don’t understand the research, the intentionality of where the plants are harvested, when and how they’re harvested, their unique growing process, and their interconnectedness.
Drapeau’s products are crafted with meticulous care, sourcing ingredients from specific geographic terrains that maximize their bioactivity and utilizing wild harvesting methods to ensure each plant's highest quality and potency. Drapeau has focused on maximizing the bioactivity of natural plant extracts so they support stem cells, and this has taken years of research while traveling to the most remote regions of the world. He’s even connected with the locals in these areas and explored the ancient origins of these plants.
He’s also discovered unique species that their ancestors have used for thousands of years, as well as biochemical differences in these plants based on where they are grown, when and how they are harvested, and how they are processed.
Then, he took his research one step further by researching each plant to measure which one had the biggest effect on supporting stem cell mobilization. The creation of his products has been a culmination of a lifetime of finding the right plants, sources, and blend of ingredients—then backing that with solid research.
There are other natural stem cell enhancers on the market, but most have borrowed Drapeau’s research, using similar-sounding ingredients to make them look the same—yet they are very different. They also lack the research to support their own formulas. The simple truth is that they aren’t formulated, developed, and intensely researched by the pioneer in natural stem cell support, Drapeau. STEMREGEN, on the other hand, delivers science-backed solutions, ingredients, and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) that bridge the wisdom of nature with cutting-edge research, supporting your body’s natural regenerative processes. You can check out more research studies done on STEMREGEN products here and here.
How Do You Increase Your Stem Cells Every Day NATURALLY and Without an Invasive Procedure?
STEMREGEN has a line of products that support stem cells using natural plant extracts and bioactive (a bioactive is a type of chemical found in small amounts in plants and certain foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, oils, and whole grains). STEMREGEN RELEASE is their core product. Drapeau’s research shows that taking two capsules of this blend of plant extracts and bioactives puts an average of 10 million additional stem cells into circulation.
His formula has been found to help stem cells increase in numbers for up to 6 hours after taking it, allowing for faster muscle recovery, enhanced repair, and keeping your body in a state of renewal. Here’s a closer look at some of the ingredients in this blend—and the science behind them.
Sea Buckthorn Berry
Harvested from the Tibetan Plateau, this is a uniquely sourced extract of sea buckthorn berry, which contains a wealth of polyphenols and anthocyanidins that have been documented to support the release of stem cells from the bone marrow.
Drapeau chose this sourcing location because he found that sea buckthorn berries grown in harsh climates at high altitudes have the highest effect on supporting stem cells. His research showed that it increased the number of stem cells circulating by 43%. The larger sea buckthorn berries found in warmer climates near the ocean were found to have little to no impact on stem cells.
Aphanizomenon Flos-Aquae (AFA)
AFA is a blue-green algae growing naturally in Klamath Lake, Southern Oregon. AFA has been known for its effect on the immune system and for supporting mental energy and clarity. The research shows that AFA extract increases the number of circulating stem cells by 25%.
Aloe Macroclada
Aloe macroclada is extracted from a unique species of aloe grown in Madagascar. It's indigenously known as vahona and has been used for centuries for a wide variety of health benefits.
There are over 128 species of aloe in Madagascar, and Drapeau’s research has shown that only Aloe macroclada increases the number of circulating stem cells by an average of 53%, which is the highest of all aloe. He is currently working on a new study, soon to be published, that shows it can increase circulating stem cells by 80%. This is a protected aloe, and Drapeau had to collaborate with local researchers and farmers to access it.
Beta-Glucan
The research shows that beta-glucan supports various aspects of stem cell function, including stem cell proliferation, release from the bone marrow, and migration into tissues. The beta-glucan used is 85% (1→3)-b-D-glucose bonds, the most potent form of beta-glucan.
Summary
Stem cells are the key to your body’s repair, recovery, and overall vitality. These powerhouse cells are responsible for healing microtears, reducing inflammation, and promoting muscle growth—keeping your body in peak condition.
But here’s the catch: as you age, your body’s natural stem cell supply drops dramatically, often by as much as 80% in your 30s and even more as you get older. This decline makes it harder for your body to bounce back from tough workouts, injuries, and the everyday wear and tear we all face—leading to slower recovery, nagging soreness, and a drop in performance.
Recent breakthroughs in stem cell science have uncovered natural ways to boost your circulating stem cells and restore your body’s repair capacity. Drapeau, a stem cell researcher, has identified plants like sea buckthorn berry, Aloe macroclada, and AFA that enhance stem cell release and support your body’s regenerative processes. Backed by research, these plants offer a safe and effective way to replenish your stem cell supply.
Here’s how you can order STEMREGEN RELEASE: (Use code BEN to get a 15% discount at this link). Leave your questions, comments and feedback below!


Hi Ben, thanks for the article.
You write “So, instead of blaming lactic acid, think of it as one of your critical players in the chain reaction that helps you recover faster and get stronger.”
So various things that athletes do in order to prevent lactic acid build up (like preloading with sodium bicarbonate or Beta Alanine) are worthless or even damaging to the muscle recovery?
?
We need more people like Martin, to speak out on a lot of these products, I’ve tried other products mentioned by Ben and given them a long term trial with no results. I like his podcast, books and articles but some products just don’t add up.
Like which ones? I rigorously test and research everything I recommend, so curious if it’s no difference in pre/post bloodwork and biomarkers, or something else Trevor?
Hi Ben
This by no means an attack on your integrity, I have bought many of your information products and found them most helpful.
At 60 my foundational principles to my health are rock solid sleep, nutrition, breathing, thoughts as well red light, infrared sauna etc.
It may be that my expectation of a product are not what they deliver and before you or anyone else jump to conclusions, I take the product for a full year with blood markers and HRV monitoring.
Currently taking oral BPC157 and TB500 form a guest on your show and will do this for the rest of 2025.
Personally I don’t want to get into individual supplements or a debate about research as from your information I continue my own deep dive into the research and then decide the cost to benefit.
So please understand I totally believe that you do your own research into every product and I will continue to listen and read to your great information.
Wishing you good health and longevity
Trevor
Don’t believe the hype. I’m 65 and I train hard, and their products did nothing for me. I ordered Stemregen’s “Release” 4 times in 2024, and the most recent order was in January of 2025 with all 3 of the suite of products (Release; Signal; & Mobilize). Ever hopeful, I guess, after hearing influencers like Ben and Asprey promote the heck out of it. Total spent: $2221.69. To say I regret my purchases would be an understatement. Probably the most disappointed and frustrated with a supplement purchase I’ve ever been. Didn’t notice any of the benefits Ben outlines above. Buyer beware.
Thank you for your honest appraisal.
Thank you, Martin, for your comment. It’s a great opportunity to provide some context for your experience.
As the founder and scientist behind Stemregen, I genuinely appreciate hearing the full range of feedback. One thing that often gets lost in the broader discussion of science is the assumption that if one person experiences benefits, everyone else should too—and if someone doesn’t, then the product must not work. That’s simply not how biology works. The data we share comes from crossover, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies designed to account for a wide range of responses. While we report averages, individual experiences range from negligible to phenomenal. For example, in an ongoing study on chronic stable congestive heart failure, all patients so far (n=10) have regained normal heart function after six months. But as the study grows, I don’t expect 100% success across the board. Your experience is an example of someone who didn’t see dramatic results.
Here are a few key things to consider:
1. Your stem cells are your repair system and always have been. Since the day you were born, they’ve been keeping you alive. Without them, your body wouldn’t heal, regenerate, or function. So your stem cells are working—this is a fact.
2. There’s a direct link between the number of circulating stem cells and the body’s ability to repair and stay healthy as we age. More circulating stem cells mean better overall repair. This is where Stemregen Release comes in—it puts an average of 10 million additional stem cells into circulation.
3. The real question is: why didn’t the stem cells that were released reach the areas where you were hoping to see benefits? Or why did you not feel the benefits?
This is where the future of stem cell research is headed—understanding what enhances or hinders stem cells’ ability to reach and repair specific tissues. The regenerative potential of stem cells is undeniable, but the factors that support or block that process are still being studied.
I truly appreciate your feedback and wish you could have experienced the results you were hoping for. But with respect, your experience doesn’t negate the thousands of others who have seen clear benefits with Stemregen—just as their success doesn’t invalidate your frustration. Also, just because you didn’t feel a difference doesn’t mean your body wasn’t benefiting. Your stem cells are working -that’s unquestionable- whether you feel it or not.
Wishing you the best on your health journey.
Christian Drapeau